In a significant advancement for user interface technology, Microsoft has unveiled an AI-powered agent for Windows 11, launching initially on Snapdragon-powered Copilot+ PCs through the Windows Insider programme on 6 May 2025. The innovative system allows users to modify settings using natural language commands, fundamentally transforming how people interact with their computers.
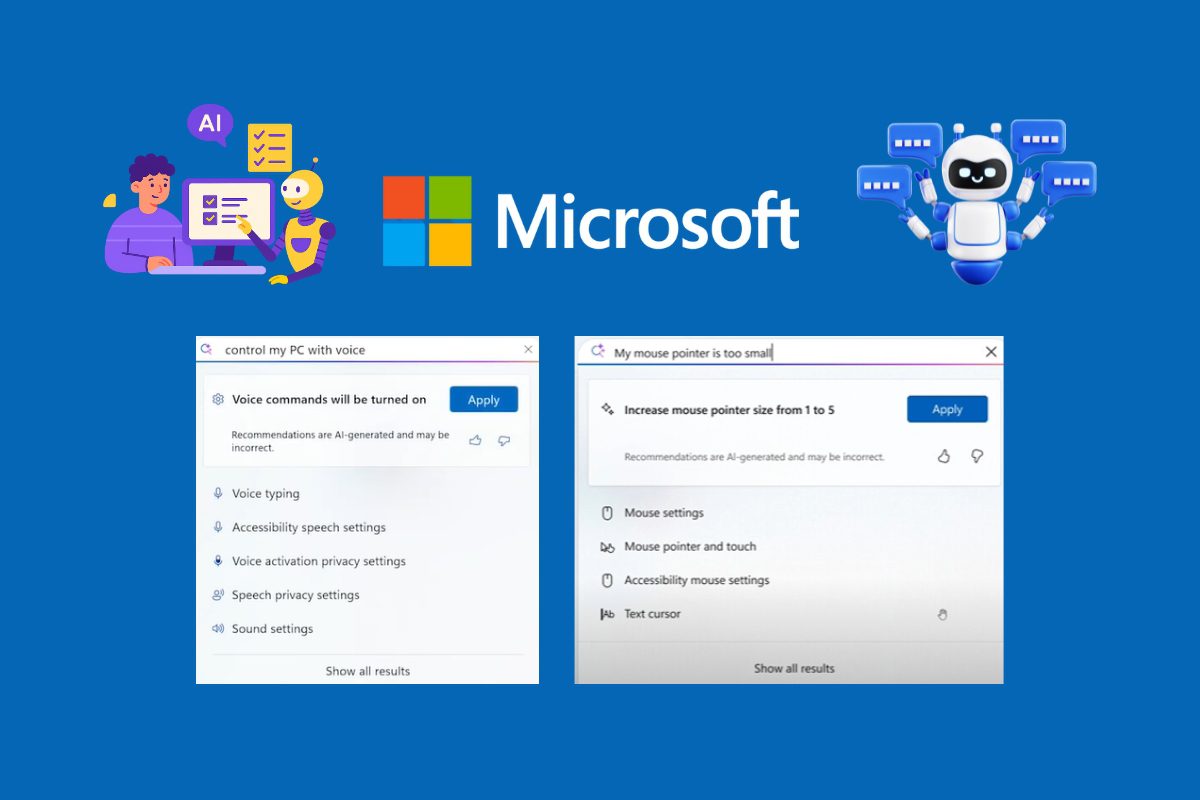
The AI agent represents a substantial departure from traditional Windows settings navigation, integrating seamlessly within the Settings app to provide a conversational interface. Users can now simply type or speak their requests, such as adjusting mouse pointer size or enabling voice control, with the AI assistant either suggesting steps or implementing changes directly upon user approval.
Navjot Virk, Microsoft’s Corporate Vice-President of Windows Experiences, highlighted the significance of this development: “We set out to solve one of the most common frustrations we hear—finding and changing settings on your PC—using the power of AI. An agent uses on-device AI to understand your intent and, with your permission, automate and execute tasks.”
The initial rollout targets Windows Insiders using Snapdragon-powered Copilot+ PCs, with plans for expansion to AMD and Intel devices in subsequent phases. While currently supporting only English language inputs, Microsoft has confirmed future updates will incorporate additional language capabilities.
Operating through a search bar positioned at the top of the Settings app, the AI agent presents relevant options and recommendations based on user queries. This design maintains the traditional Settings interface for users who prefer manual navigation whilst offering an innovative alternative for those seeking a more intuitive experience.
The integration extends beyond basic settings management, forming part of Microsoft’s broader strategy to embed AI throughout the Windows ecosystem. The company is simultaneously introducing AI-enhanced features across various Windows utilities, including dynamic lighting controls in the Photos app and automated cropping in the Snipping Tool.
A notable addition is the Copilot Vision feature, enabling users to share application windows with the AI assistant for contextual analysis and support. This functionality significantly expands the assistant’s capability to provide targeted help within specific applications and websites.
Industry analysts emphasise that the success of this AI-driven approach will largely depend on its reliability and security measures. Microsoft has addressed these concerns by implementing strict user permission requirements for any system modifications, ensuring users maintain control over their device settings.
This transformation in operating system interaction represents a significant milestone in Microsoft’s vision for more accessible technology. As the feature expands to more devices and languages, it promises to reshape how users manage their computing experience, potentially establishing new standards for human-computer interaction across the industry.
News Source: PC Gamer